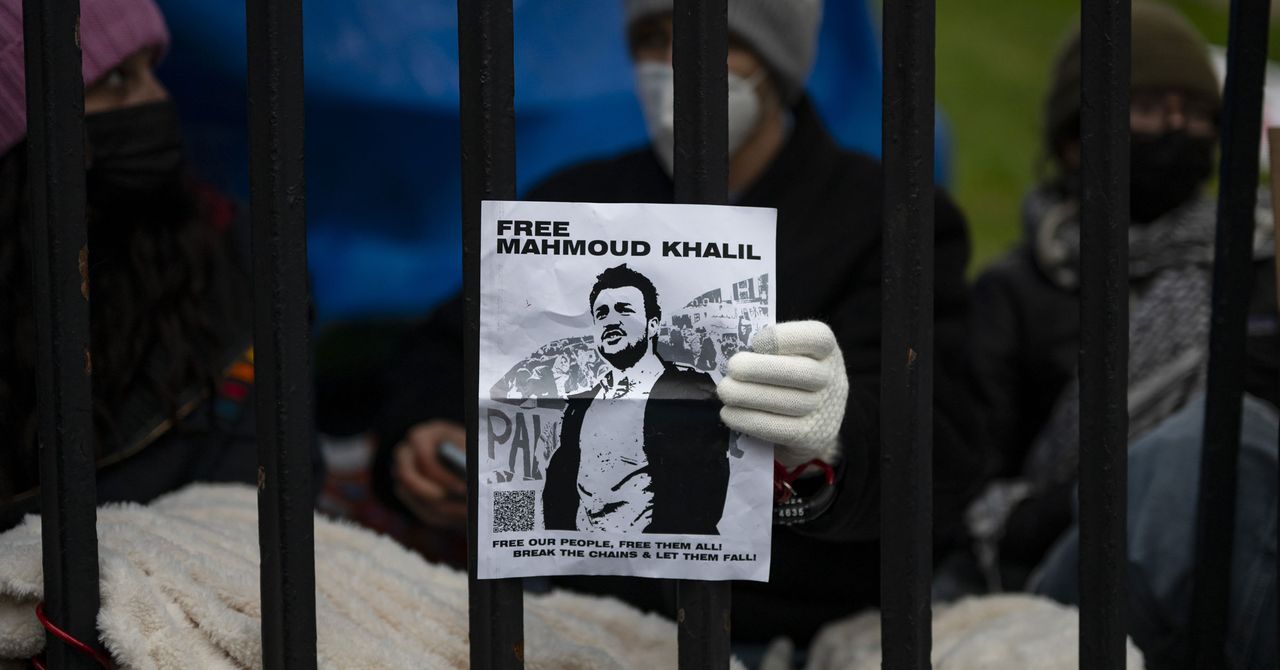
Electronics in the detention area are strictly forbidden, but Ahmed had filed paperwork the previous night to ensure that when the hearing began, she’d be allowed, as Khalil’s legal representative, to enter the courtroom with her laptop in line with EOIR policy. Nevertheless, in a sworn declaration, Ahmed says that minutes before the hearing began she was informed by the detention center staff that, on Comans’ instructions, she was forbidden from bringing her devices inside, forcing her to turn over her laptop to the faculty and enter the courtroom empty-handed. Once the hearing began, Khalil says, she sat opposite three Homeland Security attorneys, with each their own laptop.
The Hollywood image of attorneys wheeling stacks of bankers’ boxes into court is mostly antiquated, says Ahmed, whose gigabytes worth of trial data are digitally stored. “You effectively are using the technology that you have to be able to respond in real time, or inquire in real time, or to show your client in real time, what evidence the government may be talking about or responding to,” she tells WIRED. “That’s always very critical, because you want to make sure that any representation that’s being made by the other side is factual.”
Michelle Méndez, an attorney at the National Immigration Project, says the asymmetry in access to technology and resources between the government and non-citizens in court is a reflection of who controls it.
“As long as immigration courts are under the direction of the executive branch, non-citizens are never going to receive a fundamentally fair proceeding,” she says.
Méndez notes that, since February 2022, the Justice Department has required all immigration attorneys to file documents with the courts electronically, effectively establishing the expectation that attorneys should rely on digital access for court filings, case citations, and other subject matter, rather than risk expensive continuances in notoriously backlogged courts.
“The image of somebody coming in with boxes is definitely apt in those circumstances,” she says, of the sheer volume of material attorneys would be required to lug around without electronic access. “The worst-case scenario is that the attorney misses out on being able to offer the court whatever it is that the court seeks from them. They don’t have it.”
According to Ahmed, both the ICE center’s warden, Shad Rice, and Khalil’s judge denied ordering the ban, which Ahmed says she received word of only minutes before the hearing began. “When I inquired as to why, I was told that it was the immigration judge that had made the determination,” she tells WIRED. She requested to speak with the judge privately before the hearing, she says, but her request was denied.
Ahmed says Comans eventually informed her that the electronics ban had come at the request of the ICE facility. But when pressed to allow Ahmed to confer with the warden, who was also in the room at the time, the request was denied. “It seemed particularly unjust to Mr. Khalil,” she says, “as he looked at the Department of Homeland Security attorneys who had three laptops at their table.” During the hearing, she adds, the government lawyers were conducting Google searches, writing emails, and reading from papers as the proceedings took place.